How Do Kidneys Impact Bone Health?
The kidneys are a
vital organ for blood filtering and maintaining chemical balances. They also
produce hormones, which regulate blood pressure and other processes.
The kidneys are a pair
of bean-shaped organs besides the backbone and ribs on each side of the spine.
They receive blood from the body's cardiovascular system, filter out wastes and
excess water, and produce urine. Kidneys also produce hormones that regulate
blood pressure, control salt levels, and help with red blood cell production.
The kidneys filter
wastes from the blood, so they do not accumulate in the body or bloodstream.
What Is Mineral And Bone Disorder?
A mineral and bone
disorder, also known as a metabolic disease, is a chronic condition that
results in the body not having enough or too much of certain minerals. A
genetic disorder may cause one type of mineral and bone disorder (such as
osteoporosis), but an injury or disease causes others. Osteoporosis is the most
common type of mineral and bone disorder.
Osteoporosis is a
disease of the bones that causes them to become weak and prone to fractures. It
usually affects older people but can also affect younger people who have been
inactive for long periods or have taken certain medications.
Symptoms Of A Mineral And Bone Disorder
Mineral and bone
disorders can be difficult to diagnose, depending on their cause, but they
usually include the following symptoms:
- Itchy skin
- Bone pain
- Weak bones that break easily
- Blocked blood vessels
- Heart problems
- Anemia
- Nerve problems
- Difficulty fighting off germs
In general, mineral
and bone disorders such as osteomalacia are not immediately life-threatening,
but they can cause discomfort during everyday activities like sitting or
walking for prolonged periods.
The Functions Of The Kidney In Maintaining Bone Structure
The kidney produces
several hormones that play a part in maintaining bone structure. One such
hormone, erythropoietin (EPO), stimulates the bone marrow to produce better red
blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body and are essential
for healthy bones.
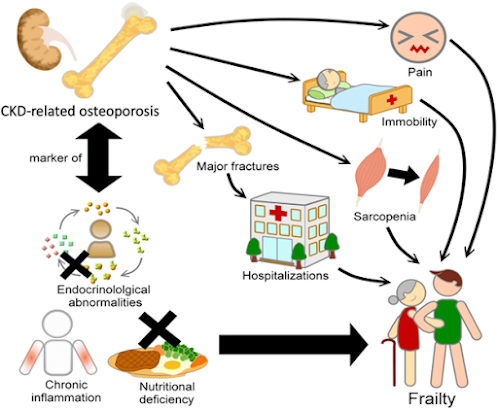
Renal Osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy
occurs when the bones are affected by a disease resulting from impaired kidney
function. The kidneys regulate the blood levels of calcium and phosphate, which
are necessary for bone growth. When these levels are not regulated properly,
bone density is reduced, and renal osteodystrophy occurs.
Roles Of The Kidney In The Building, Remodeling, And Repair Of Bone
- The kidney is an important organ for maintaining
homeostasis of calcium and phosphate.
Kidneys eliminate
excess amounts of calcium and phosphate, which are the building blocks of
bones. If a person has a healthy diet, the kidneys can usually maintain a
normal level of these minerals. A person might develop hypercalciuria or
hyperphosphaturia if there is too much calcium and phosphate in the kidneys.
- The kidney plays a role in regulating bone health by
developing activated vitamin D.
The kidney regulates
blood pressure, balances the production of salt and potassium, and controls the
excretion of urine by the body.
"Additionally, it
regulates bone health by generating activated vitamin D."
The kidneys can
convert vitamin D into calcitriol, a metabolically active vitamin D, and
release it into the bloodstream. This metabolized vitamin D is responsible for
absorbing calcium and phosphorus in our diet.
- The kidney produces a protein called Klotho, which
supports bone formation and remodeling.
A hormone produced by
the kidneys called klotho regulates bone formation and remodeling. A new study
published in Cell Metabolism shows that this hormone also increases lifespan
and combats aging-related diseases. The study found that klotho regulates the
breakdown of bone tissue, which also plays a role in aging.
- The kidneys regulate bone growth by producing the
growth-inducing protein called bone morphogenetic protein 7.
A study published in
Cell Reports has found that the protein BMP7, which the kidney produces,
regulates bone growth by stimulating bone formation. Researchers found that
when levels of BMP7 were reduced, mice experienced reduced bone length, size,
and density. This discovery could have important implications for human
diseases and disorders like rickets, osteogenesis imperfecta, osteoporosis, and
arthritis.
A new study published
in Cell Reports has shown that decreasing bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7)
results in smaller and lighter bones. The discovery may have important
implications for the future of bone treatments.
- The kidney synthesizes erythropoietin, a protein that
promotes bone development and helps fractures heal.
The kidney produces
erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone that stimulates the formation of red blood
cells. These newly formed red blood cells deliver oxygen to the kidneys, bones,
and muscles. Epoetin alpha is used to treat anemia caused by chronic kidney
disease and other forms of anemia. Treatment with this drug has improved the
quality of life for patients with severe anemia.
The Causes Of Chronic Kidney Disease That Affects Bone Health
Chronic kidney disease
is a progressive, irreversible, and often fatal disease that causes a gradual
loss of kidney function, leading to high blood pressure and anemia. It also
puts sufferers at risk for bone health problems, including fractures and
osteoporosis.
The causes of chronic
kidney disease are not fully understood, but it is known that there are many
factors involved. Diabetes, high blood pressure, Obesity, smoking, and other
lifestyle choices are all risk factors for the disease.
How To Prevent Or Improve Chronic Kidney Disease To Protect Your Bones And Other Body Parts?
Chronic kidney disease
can be affected by diabetes, high blood pressure, and chronic urinary tract
infections. In addition, inherited diseases such as polycystic kidney disease
can cause chronic kidney disease.
Here are some preventive measures that may help lower your risk of chronic kidney disease:
1. Be Physically Active
A healthy lifestyle includes regular physical
activity. This reduces the risk of developing diseases, such as diabetes and
heart disease, and helps increase overall health and well-being.
Before you begin an exercise program, it is
important to determine which physical activity interests you most. Many
recreational activities include walking, running, swimming and biking.
Consult with a physician before beginning any
exercise program or when there is any possibility that your medical condition
might make it difficult for you to engage in physical activity.
- Eat Healthily
There are many reasons why it can be difficult
to make healthy food choices, including the availability of unhealthy options.
In this section, you will discover tips for making healthier food choices.
The first step in making healthy food choices
is to read nutrition labels and understand the nutritional content of the food
you are considering. Knowing this information can help you identify if a food
item has too much sugar or salt and make an informed decision about whether or
not it is something you want to eat.
The second tip is to eat more vegetables and
fruits because they contain few calories, lots of vitamins and minerals, and
fiber which helps control your appetite.
According to a 2012 article in the journal
Obesity, researchers found that drinking water before meals can increase
feelings of fullness and lower caloric intake during meals. The more full you
feel, the less likely you will overeat.
- Give Up Smoking And Alcohol
Craving is a powerful sensation that can lead
people who want to quit smoking and drinking alcohol to relapse into their old
habits. There are ways to reduce cravings, such as avoiding situations that
trigger them and replacing bad habits with healthy ones.
It would be best if you tried to keep yourself
busy and occupied by doing other things you enjoy. This will distract you from
your cravings and help you not give in to them. It would also be best if you
stayed away from people who smoke or drink alcohol because they will make your
cravings stronger.
- Control Your Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic disease that prevents
the body from metabolizing sugar normally. It is either caused by insufficient
insulin production by the pancreas or by unresponsive cells.
There are two types of diabetes, type 1 and
type 2. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in childhood or adolescence and is
caused by the body's immune system mistakenly attacking healthy cells in the
pancreas. Type 2 is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for up to 95
percent of all cases.
The disease diabetes has a variety of
symptoms, including increased thirst, hunger, frequent urination, blurred
vision, slow healing wounds, and weight loss. The most common form is Type 2
diabetes. It accounts for 90% of all cases and usually occurs in adults over
40. The less common but still significant Type 1 diabetes generally starts in
children or young adults and requires daily insulin injections to keep blood
sugar levels under control.
The first step to controlling diabetes is to
count your carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are present in starchy foods like
bread, pasta, potatoes, and rice. The American Diabetes Association recommends
limiting these foods to less than 20-25 grams per meal and 40-50 grams of carbs
per day.
Before eating anything, measure your blood
sugar levels and record the numbers on a sheet of paper for future reference.
This will help you determine whether you need to consume fewer carbohydrates at
certain times of the day or whether you need to administer more insulin.
- Control Your Blood Pressure
Several therapeutic diets are available for
the treatment of hypertension. These diets include foods rich in potassium,
magnesium, and calcium, such as bananas, avocados, broccoli, and spinach.
Another way to reduce sodium intake is to cut
back on salt. People who try to reduce their salt intake by using a salt
substitute or buying low-salt foods may find these methods ineffective.
Avoiding processed foods and choosing whole foods such as fruits, vegetables,
and grains is a better option.
- Manage Your Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a type of lipid in the blood
and helps transport fat-soluble vitamins to cells throughout the body. It is
also an important component of cell membranes, protecting from infection by
bacteria and viruses. Eating healthy food low in saturated and trans fat can
help lower cholesterol levels.
How Would I Know If I Have An Unhealthy Kidney Or Risk Factors That May Lead To Poor Bone Health?
It is important to
speak to your doctor about possible kidney disease or bone health concerns if
you experience any of the following symptoms.
Some of the common
symptoms of kidney disease are:
- Blood in the urine
- Pain in the back, side, or abdomen
- Frequent urination
- Weight loss and fatigue.
Other risk factors for
poor bone health include:
- Osteoporosis (bone thinning)
- Diet low in calcium and vitamin D.
Conclusion & Takeaway: What You Need To Know About The Link Between The Kidney And Bone Health
The kidneys regulate
the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body. This is necessary for healthy
bone formation. To maintain a healthy kidney function, you should always drink
plenty of water and maintain a healthy diet with a surplus of calcium, vitamin
D, and protein.








No comments:
Post a Comment